 Image credit: CD-GraB Paper Figure 1
Image credit: CD-GraB Paper Figure 1Abstract
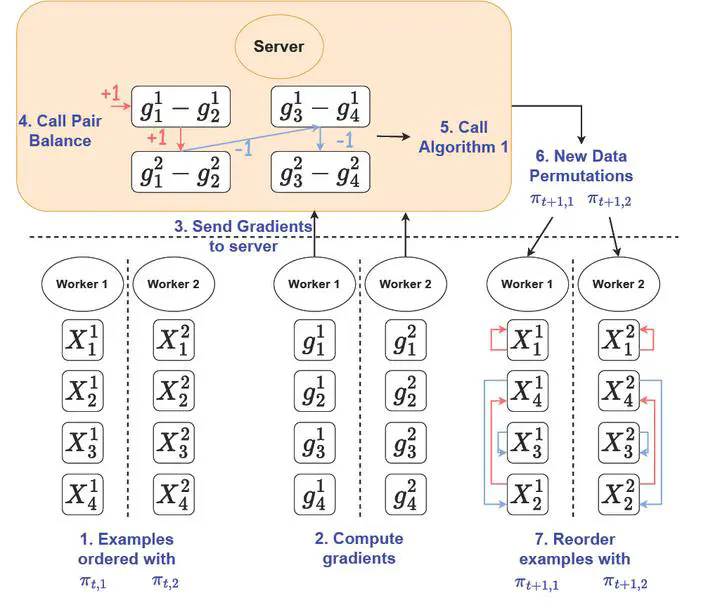
Recent research on online Gradient Balancing (GraB) has revealed that there exist permutation-based example orderings that are guaranteed to outperform random reshuffling (RR). Whereas RR arbitrarily permutes training examples, GraB leverages stale gradients from prior epochs to order examples — achieving a provably faster convergence rate than RR. However, GraB is limited by design. While it demonstrates an impressive ability to scale-up training on centralized data, it does not naturally extend to modern distributed ML workloads. We therefore propose Coordinated Distributed GraB (CD-GraB), which uses insights from prior work on kernel thinning to translate the benefits of provably faster permutation-based example ordering to distributed settings. With negligible overhead, CD-GraB exhibits a linear speedup in convergence rate over centralized GraB and outperforms baselines empirically, including distributed RR, on a variety of benchmark tasks.